The gold standard for blood glucose monitoring in diabetic patients: Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
Release time:
2025-01-06

The Origin of Glycated Hemoglobin
The subfraction HbA1c, a nonenzymatic glycation at the amino-terminal valines of the beta-chain, was identified by Iranian scholar Ranbar et al in the 1960s as a minor "abnormal fast-moving hemoglobin band" in diabetic patients during routine screening for hemoglobin variants.
Definition of Glycated Hemoglobin
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is a product of the slow, continuous, non-enzymatic binding of glucose to hemoglobin in red blood cells, and this binding is irreversible. The measurement reflects the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has bonded with glucose relative to the total hemoglobin, with a normal reference range of 4 to 6%. Since the lifespan of red blood cells is 120 days, HbA1c can indicate the average blood glucose levels indirectly over the past three months.
The Clinical Significance of Glycated Hemoglobin
For evaluating the overall glycemic control of patients over the past 2 to 3 months. HbA1c reflects the degree of long-term blood glucose control accurately and plays a crucial role in glucose monitoring.
For predicting the Risk of Chronic Complications in Diabetes.HbA1c levels are closely associated with the development of chronic complications in diabetes, particularly microvascular complications. Therefore, HbA1c levels serve as an important indicator for predicting such complications. Observations reveal that when HbA1c is below 7%, the risk of chronic complications is minimal, but once HbA1c exceeds 7%, the risk of chronic complications increases significantly.
As the diagnostic indicator for diabetes. In 2010, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) included HbA1c ≥6.5% as one of the diagnostic criteria for diabetes in its diabetes management guidelines. In 2011, the World Health Organization (WHO) also recommended HbA1c ≥6.5% as a cut-off for diagnosing type 2 diabetes in non-pregnant adults. At the 24th National Academic Conference of the Chinese Diabetes Society, it was officially announced the adoption of HbA1c as a diagnostic standard for diabetes.
For differential diagnosis of stress induced hyperglycemia, such as myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular accidents, which might cause temporary increases in blood glucose, but HbA1c may not necessarily increase in such patients.
Control Range of Glycated Hemoglobin
Generally, the following ranges for HbA1c levels are used to indicate the quality of glycemic control in individuals with diabetes:
•4% to 6%: Indicates normal glycemic control. This range is typically seen in individuals without diabetes or those with very well-controlled diabetes.
•6% to 7%: Suggests relatively good glycemic control. It is often targeted by people with diabetes to minimize the risk of long-term complications.
•7% to 8%: Indicates moderate glycemic control. This may be acceptable for some patients, but tighter control may be recommended depending on individual health condition.
•8% to 9%: Signals suboptimal glycemic control. Individuals in this range should consider improving their diet, increasing physical activities, and consulting with healthcare professionals to adjust their treatment plan as necessary.
•>9%: Represents poor glycemic control, which is a significant risk factor for the development and progression of chronic complications associated with diabetes.
Advantages of JIEZLAB microfluidic HbA1c test kits on biochemistry analyzers
1. JIEZLAB HbA1c can use 5μL capillary blood or anticoagulant venous whole blood.
2. JIELAB HbA1c exhibits excellent repeatability of ≤3%, and the table below presents the repeatability data for the high and low value.
| Low value (NGSP unit) | Hight value (NGSP unit) |
5.6% | 8.2% | |
5.7% | 8.3% | |
5.7% | 8.1% | |
5.7% | 8.2% | |
5.6% | 8.0% | |
5.6% | 7.8% | |
5.6% | 8.0% | |
5.6% | 8.0% | |
5.9% | 8.1% | |
5.7% | 8.0% | |
Avg | 0.0567 | 0.0807 |
SD | 0.0009 | 0.0014 |
CV | 1.67% | 1.76% |
3.JIEZLAB HbA1c boasts high accuracy.
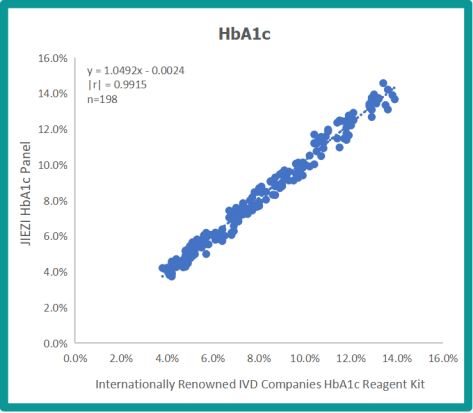
Microfluidic HbA1c test in JIEZLAB Microfluidic Biochemistry Analyzer offers highly repeatable and accurate results within 14 minutes. Only 5μL anticoagulant whole blood or capillary blood is required for testing. Besides HbA1c, biochemicals and other proteins like CRP, urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) can all be tested in JIEZLAB Microfluidic Biochemistry Analyzer. Find more information of our products by visiting website or contact us at info@jiezlab.com or 0086-400-002-0030.







